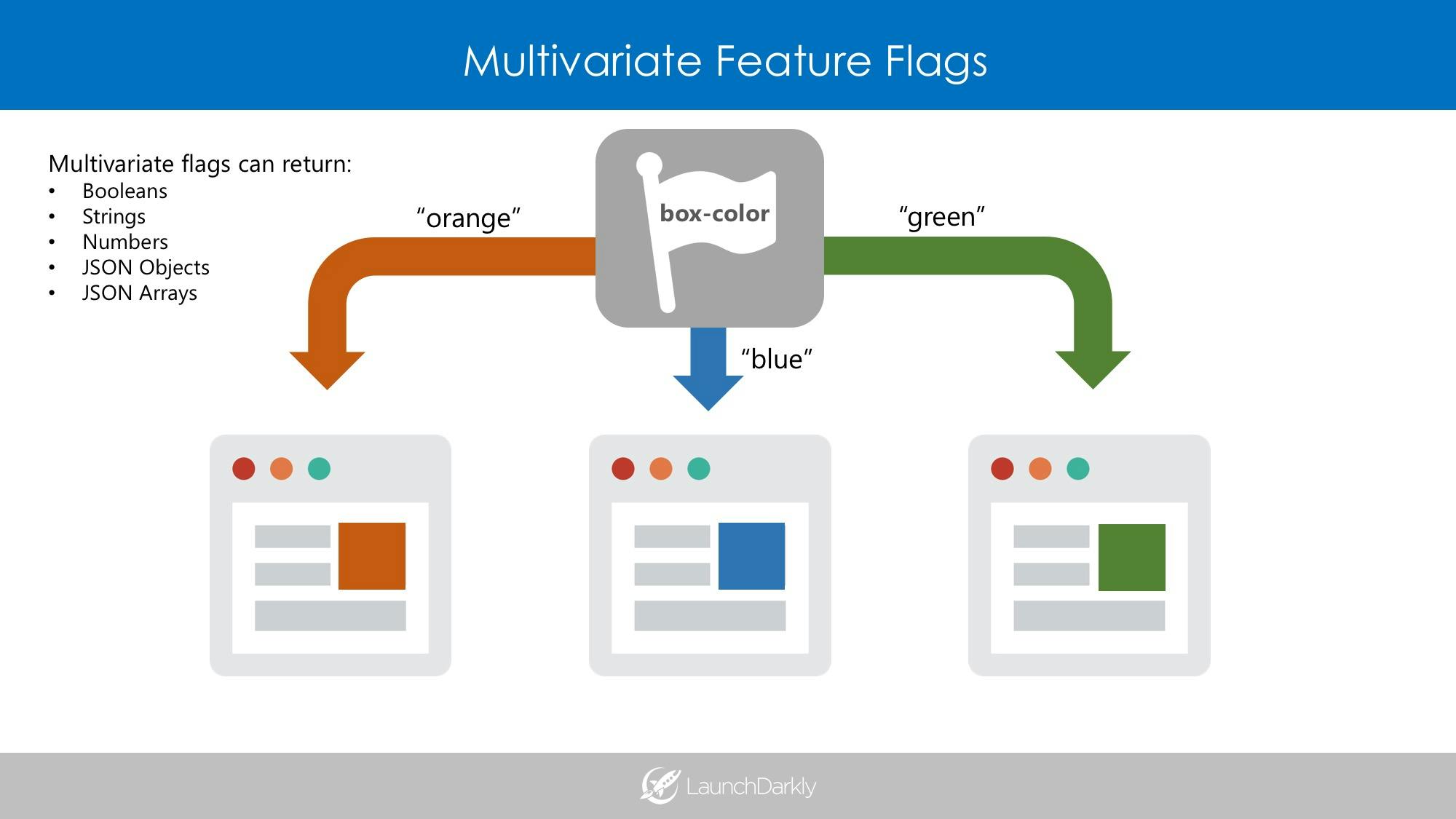
Traditionally, software teams have used feature flags/toggles to control simple rollouts and enable kill switches. Boolean values were used for “on” or “off”, “true” or “false”. With the introduction of multivariate flags, developers have been experimenting with serving rich values via these flags: strings, numbers, JSON objects, and JSON arrays. This has opened up a whole new world of dynamic application management.
Use Cases
Using feature flags to manage dynamic applications opens up many powerful and interesting use cases, for example:
- Manage features in a pricing plan
- Customize pricing based on user segment Apply coupons and discounts based on user actions or holiday sales
- Allow users to personalize their own experiences
- Manage CSS styling to test colors, layouts, and elements
- Control conditional logic separately from your code base
The Multivariate Flag
A multivariate feature flag has two primary benefits: you can customize the number and type of variations returned.
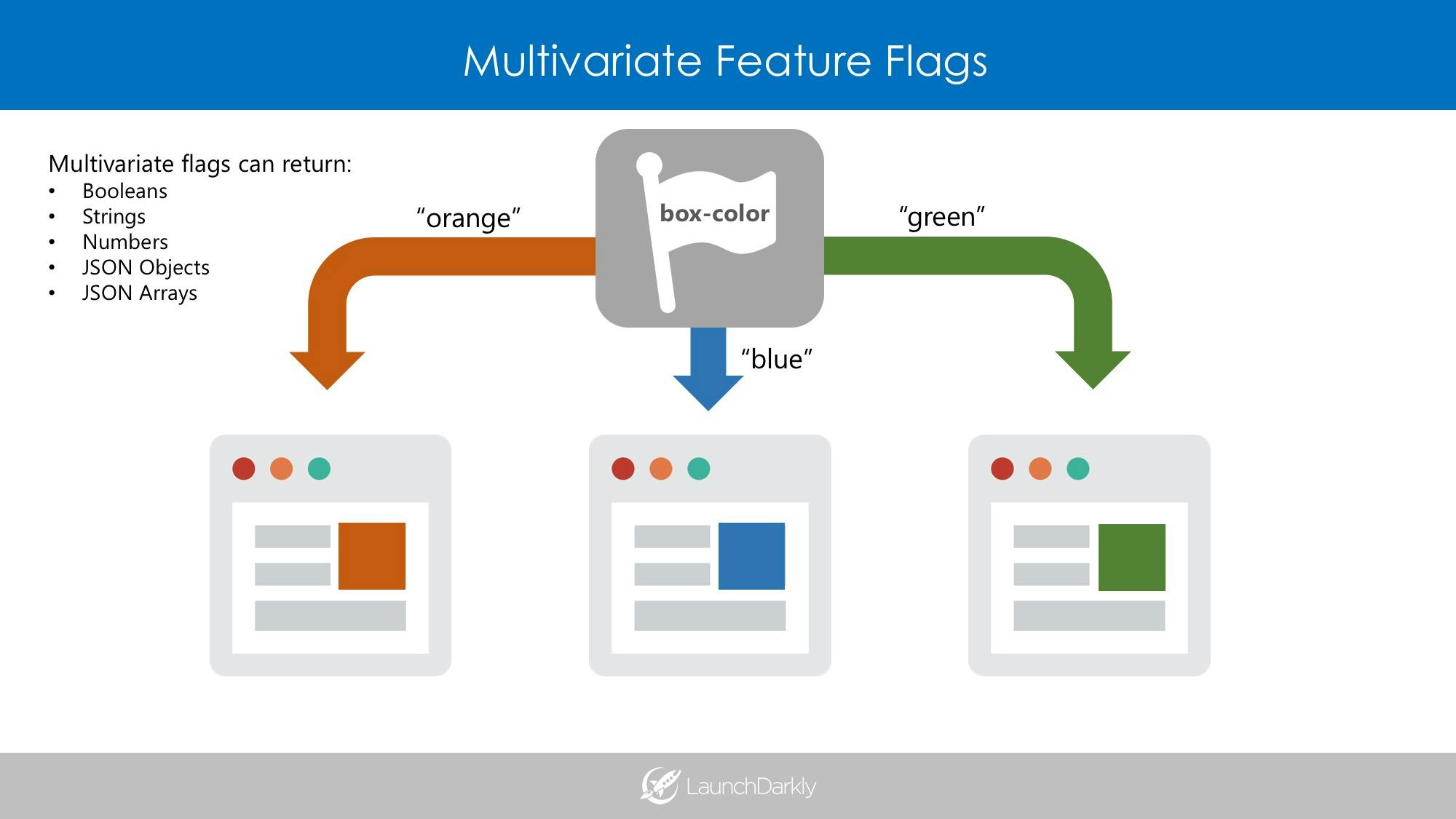
Let's first look at a simple example. This feature flag calls the variation method to determine which variation the user should get for a “checkout.flow” feature flag.
Here, the user “bob@example.com” will either see a one-click, two-click, or original checkout based on the string value returned by the feature flag:
show_feature = ldclient.get().variation("checkout.flow", {"key": "bob@example.com"}, “original-checkout”)
if show_feature == “one-click-checkout”:
# show the one click checkout feature
else if show_feature == “two-click-checkout”:
# show the two click checkout feature
else:
# show the original checkoutServing Dynamic Values
Now, let's use a feature flag to insert prices into a pricing page based on some attributes of a the user. We'll call this feature flag “plan.price”.
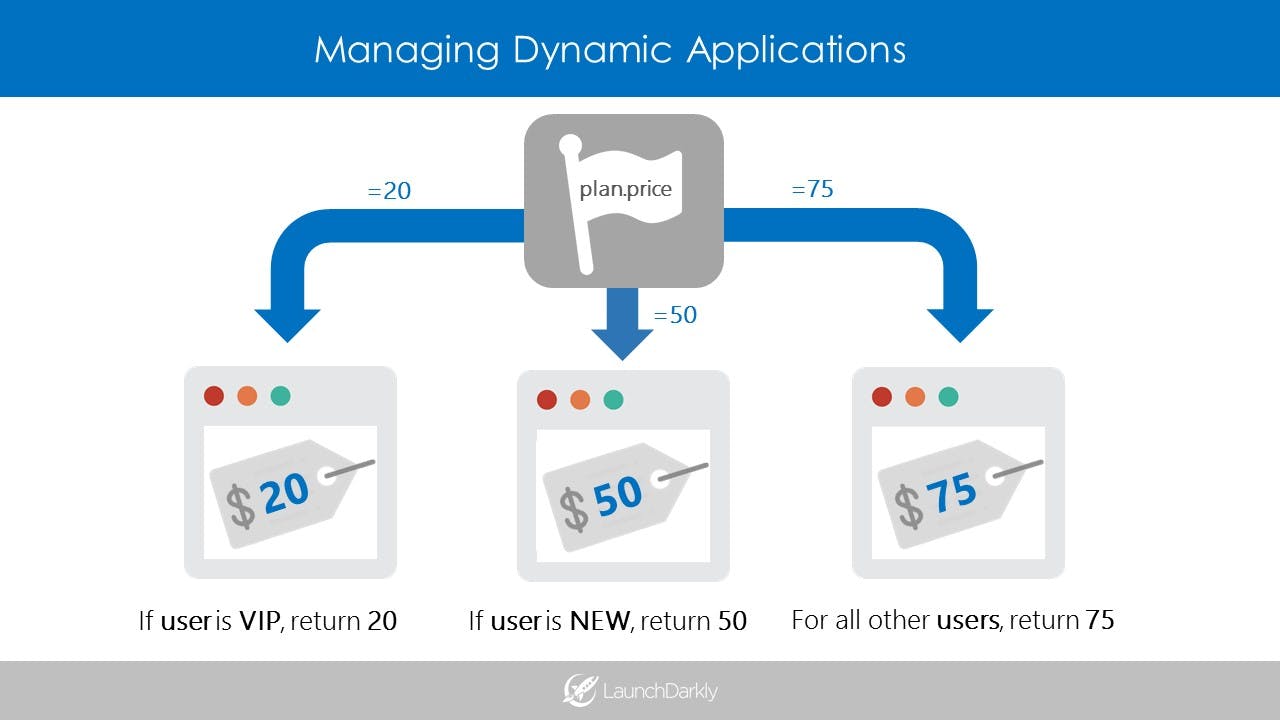
Here, the user will receive a price of $20, $50, or $75 depending on whether they match a particular targeting rule.
price = ldclient.get().variation("plan.price", {"key": "bob@example.com"}, “75”)
if price:
print('price =', price)
# shows the dynamic feature flag variation
else:
foo()
# if no variation existsFor a more advanced use case, these values (20, 50, 75) could be used to populate other pricing dependencies, like a customer invoice and account limits.
Best Practices
Of course, you should not use feature flags as a secondary database, but they could be useful as a way to personalize feature targeting without tying that logic into your codebase. This allows you to rapidly change pricing models, test color schemes, and configure complex features without having to redeploy.